Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
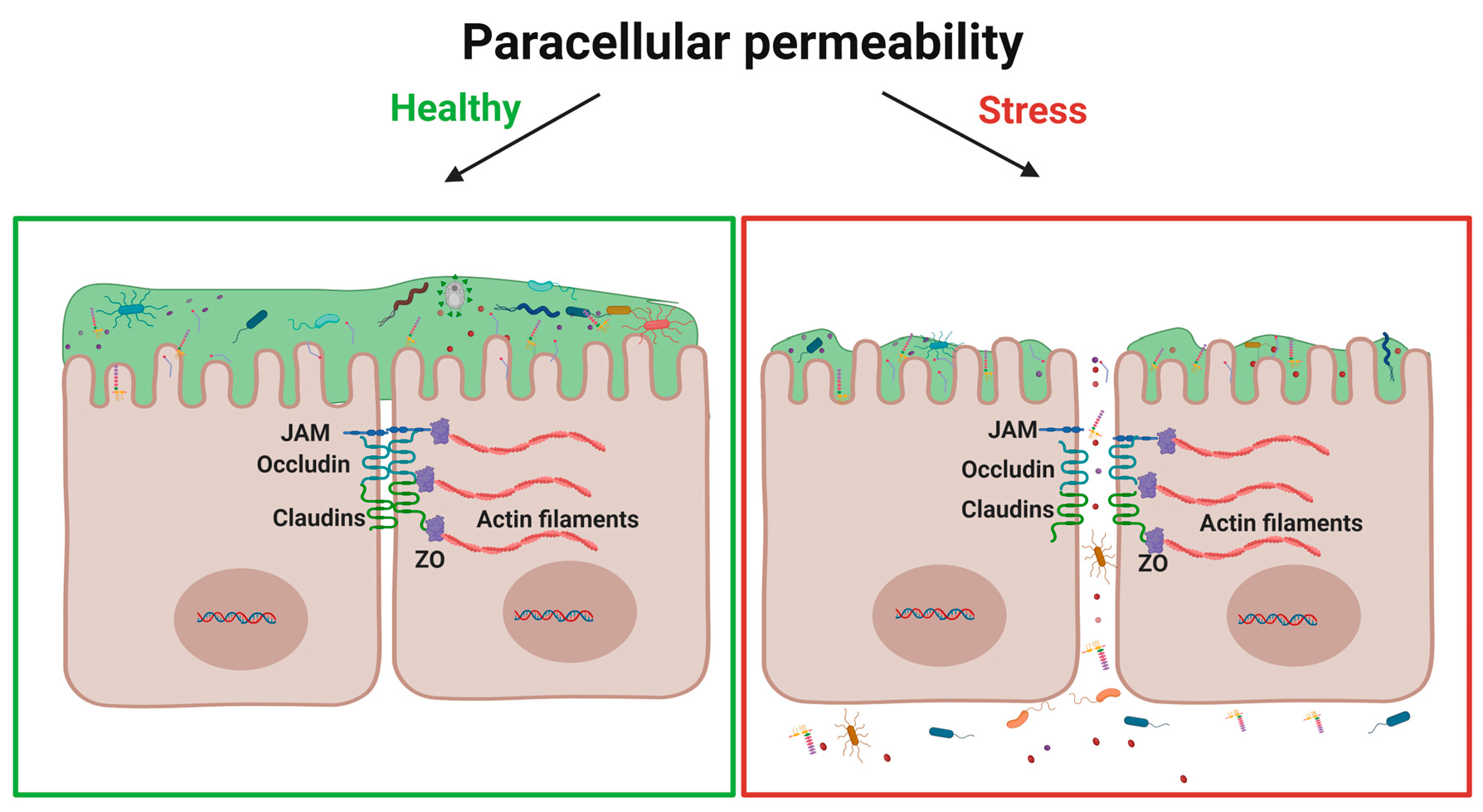
The neurovascular unit (NVU) is a conceptual framework that has been proposed to better explain the relationships between the neural cells and blood vessels in the human brain, focused mainly on the brain gray matter. The major components of the NVU are the neurons, astrocytes (astroglia), microvessels, pericytes, and microglia. In addition, we believe that oligodendrocytes should also be included as an indispensable component of the NVU in the white matter. Of all these components, astrocytes in particular have attracted the interest of researchers because of their unique anatomical location; these cells are interposed between the neurons and the microvessels of the brain. Their location suggests that astrocytes might regulate the cerebral blood flow (CBF) in response to neuronal activity, so as to ensure an adequate supply of glucose and oxygen to meet the metabolic demands of the neurons. In fact, the adult human brain, which accounts for only 2% of the entire body weight, consumes approximately 20–25% of the total amount of glucose and oxygen consumed by the whole body. The brain needs a continuous supply of these essential energy sources through the CBF, because there are practically no stores of glucose or oxygen in the brain; both acute and chronic cessation of CBF can adversely affect brain functions. In addition, another important putative function of the NVU is the elimination of heat and waste materials produced by neuronal activity. Recent evidence suggests that astrocytes play pivotal roles not only in supplying glucose, but also fatty acids and amino acids to neurons. Loss of astrocytic support can be expected to lead to malfunction of the NVU as a whole, which underlies numerous neurological disorders. In this review, we shall focus on historical and recent findings with regard to the metabolic contributions of astrocytes in the NVU.

Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods, Microbial Cell Factories

Cell-free Macromolecular Synthesis

Cells, Free Full-Text
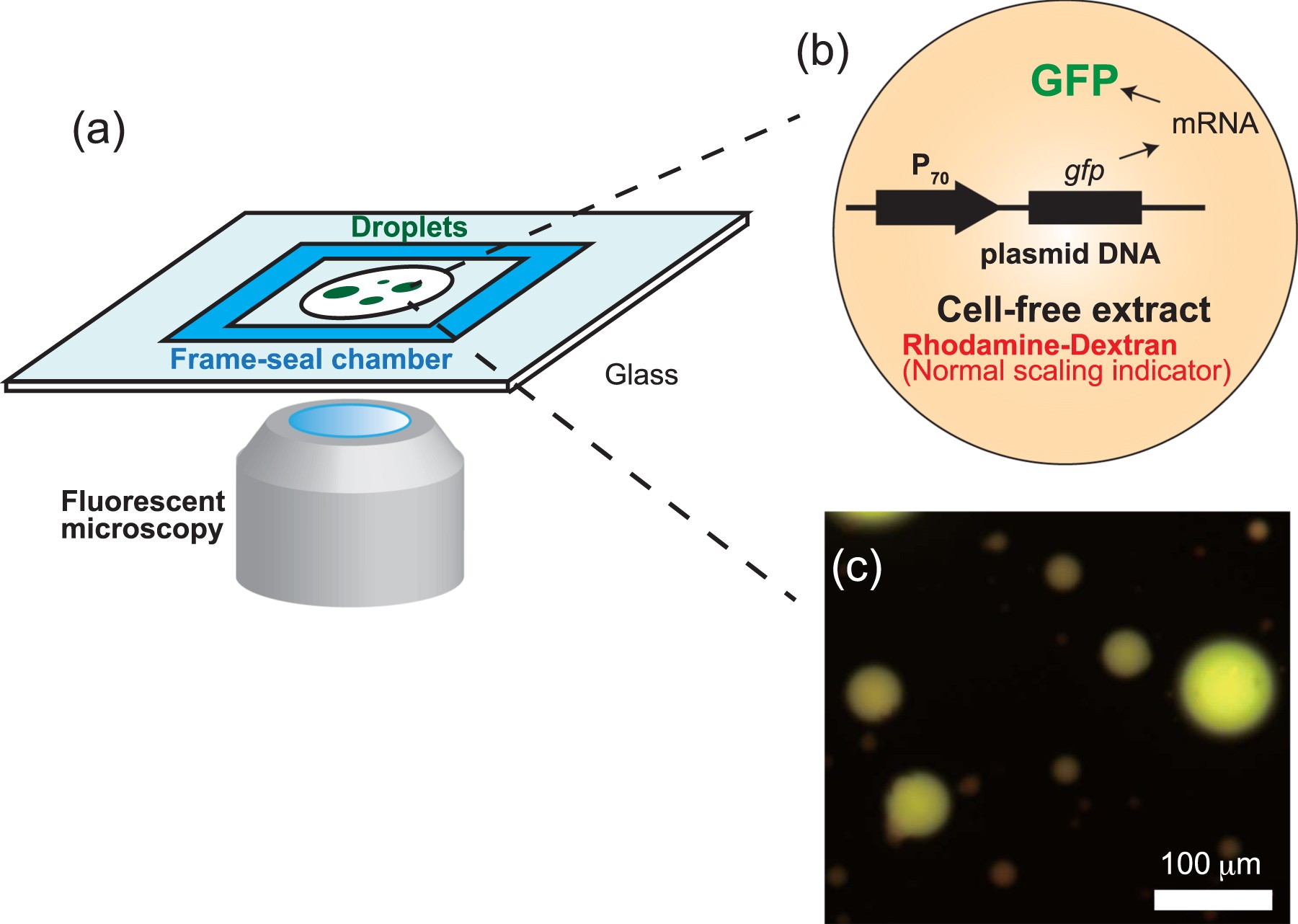
Anomalous Scaling of Gene Expression in Confined Cell-Free Reactions
Oreilly Essential System Administration 3Rd Edition Aug 2002 Rar - Colaboratory
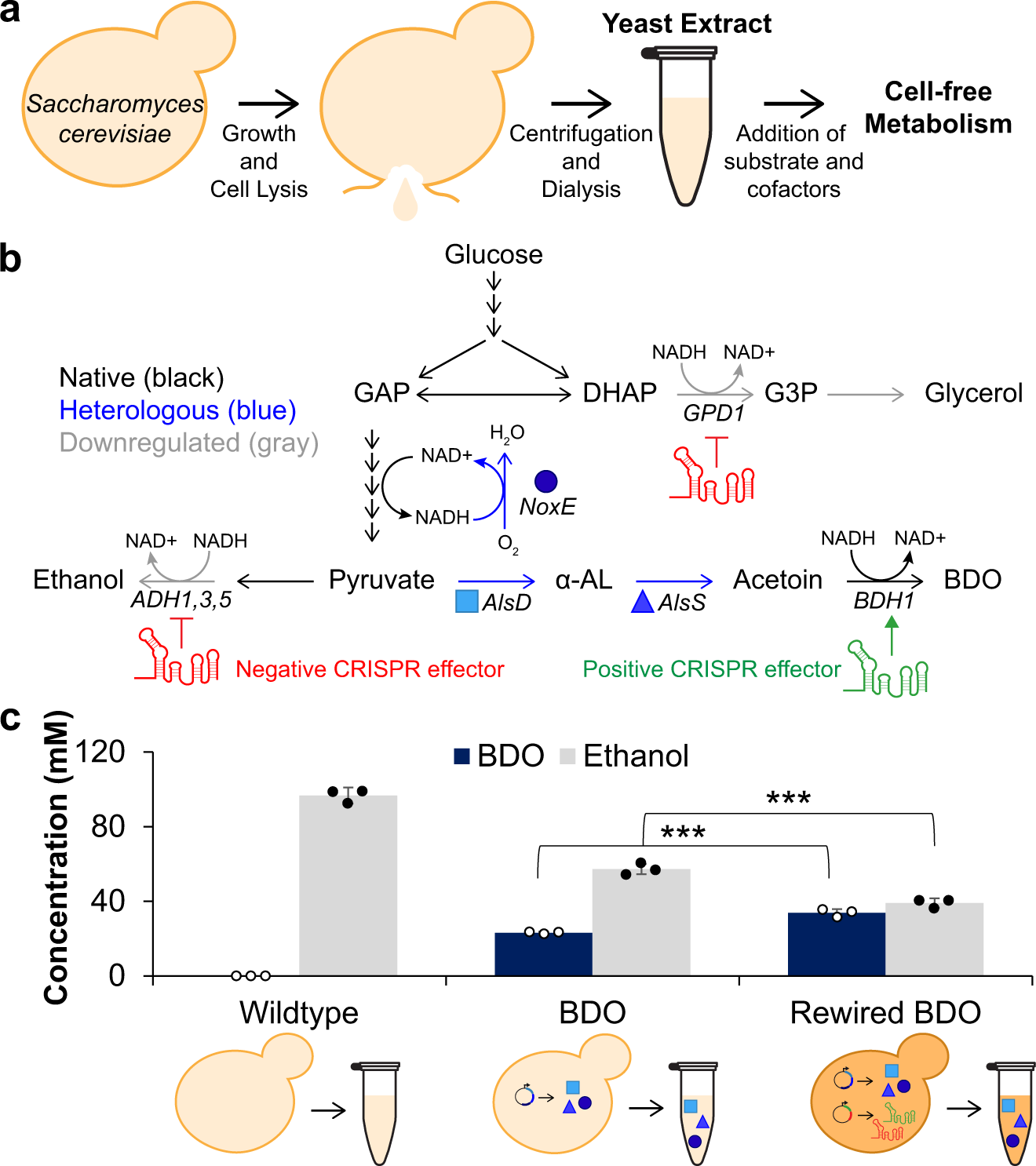
An integrated in vivo/in vitro framework to enhance cell-free biosynthesis with metabolically rewired yeast extracts
THE CELL : PAUL REVERE11 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
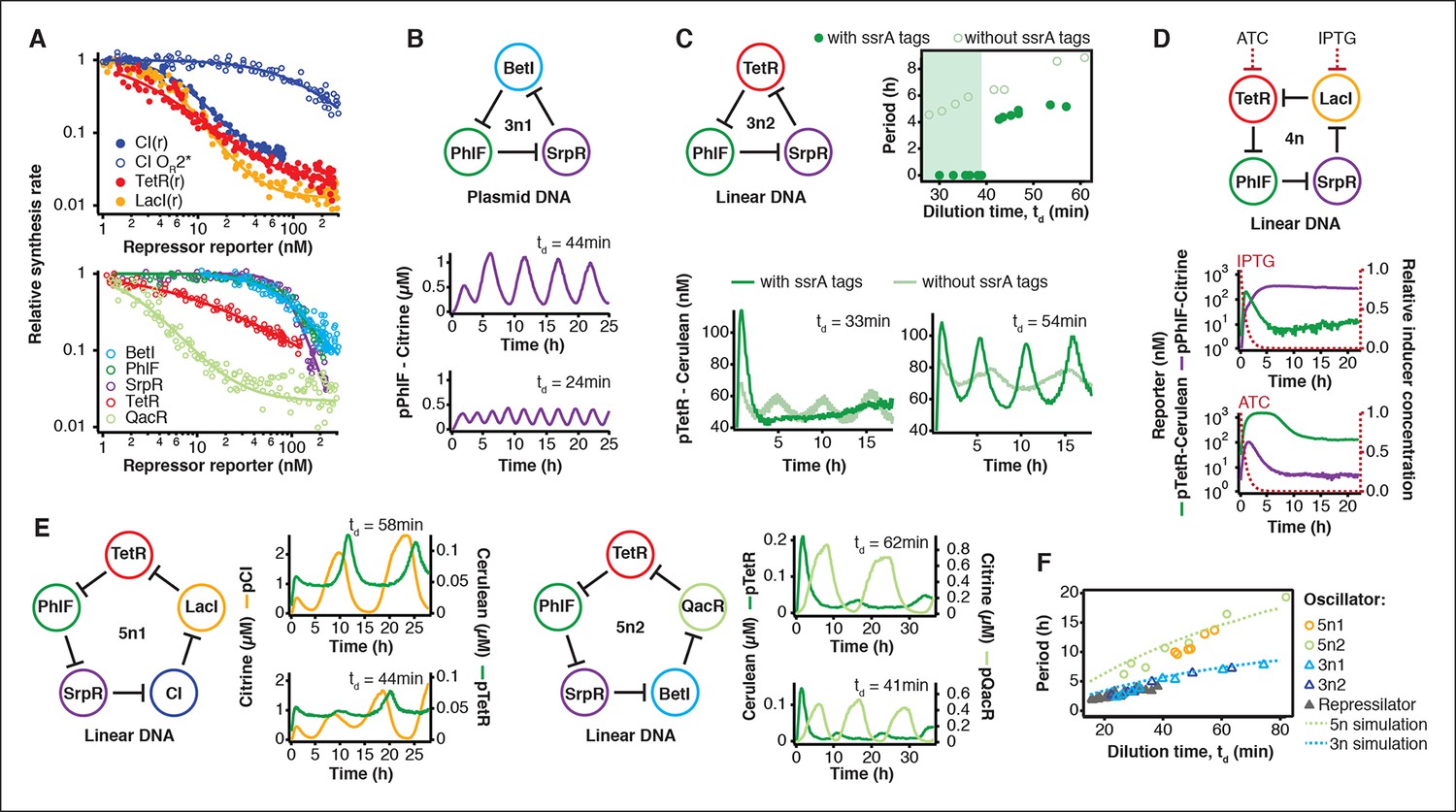
Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.

Five-Year Outcomes for Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas with CAR T-Cell Therapy

PDF) Comparative separation methods and biological characteristics of human placental and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in serum-free culture conditions
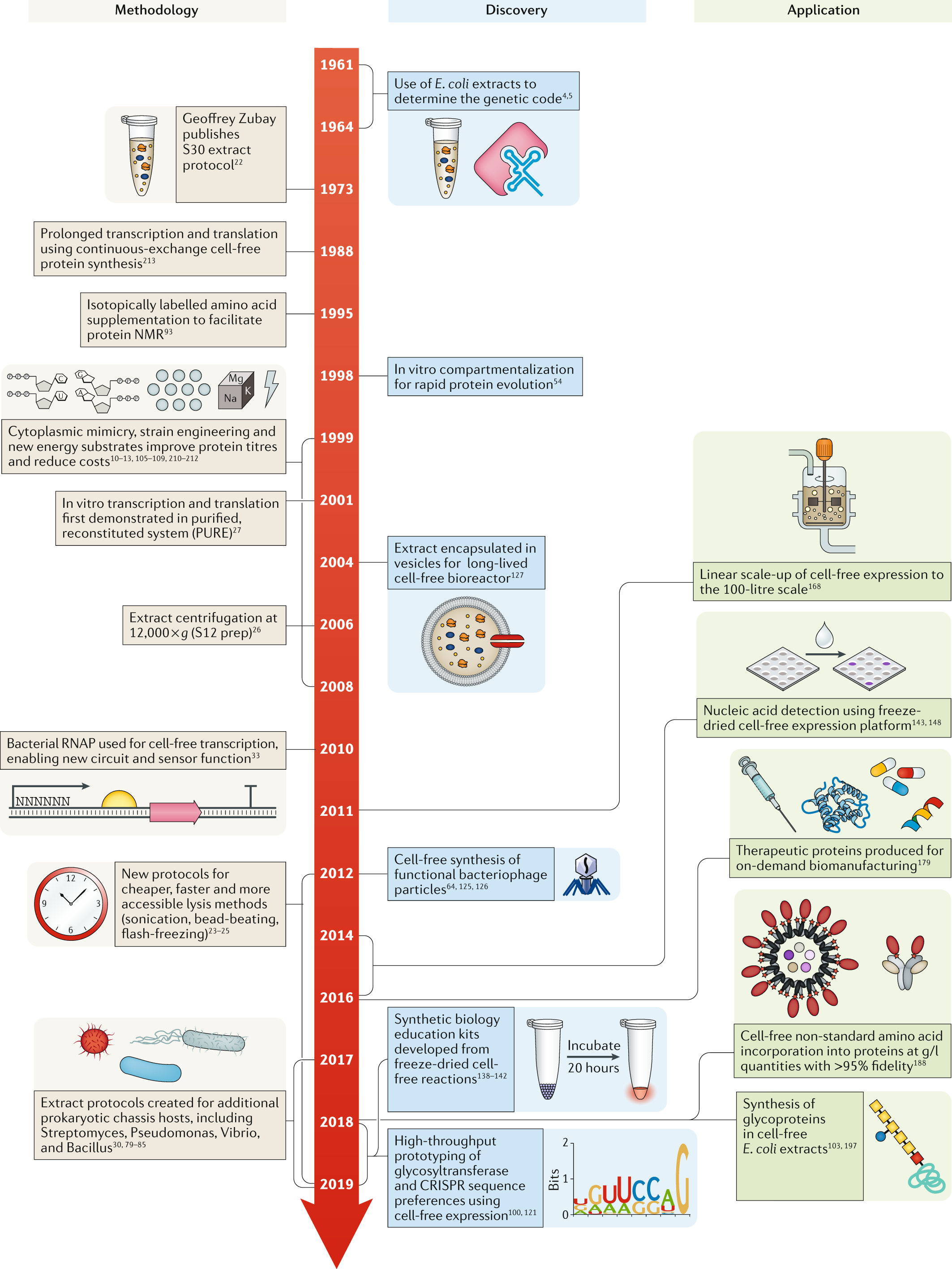
Cell-free gene expression: an expanded repertoire of applications
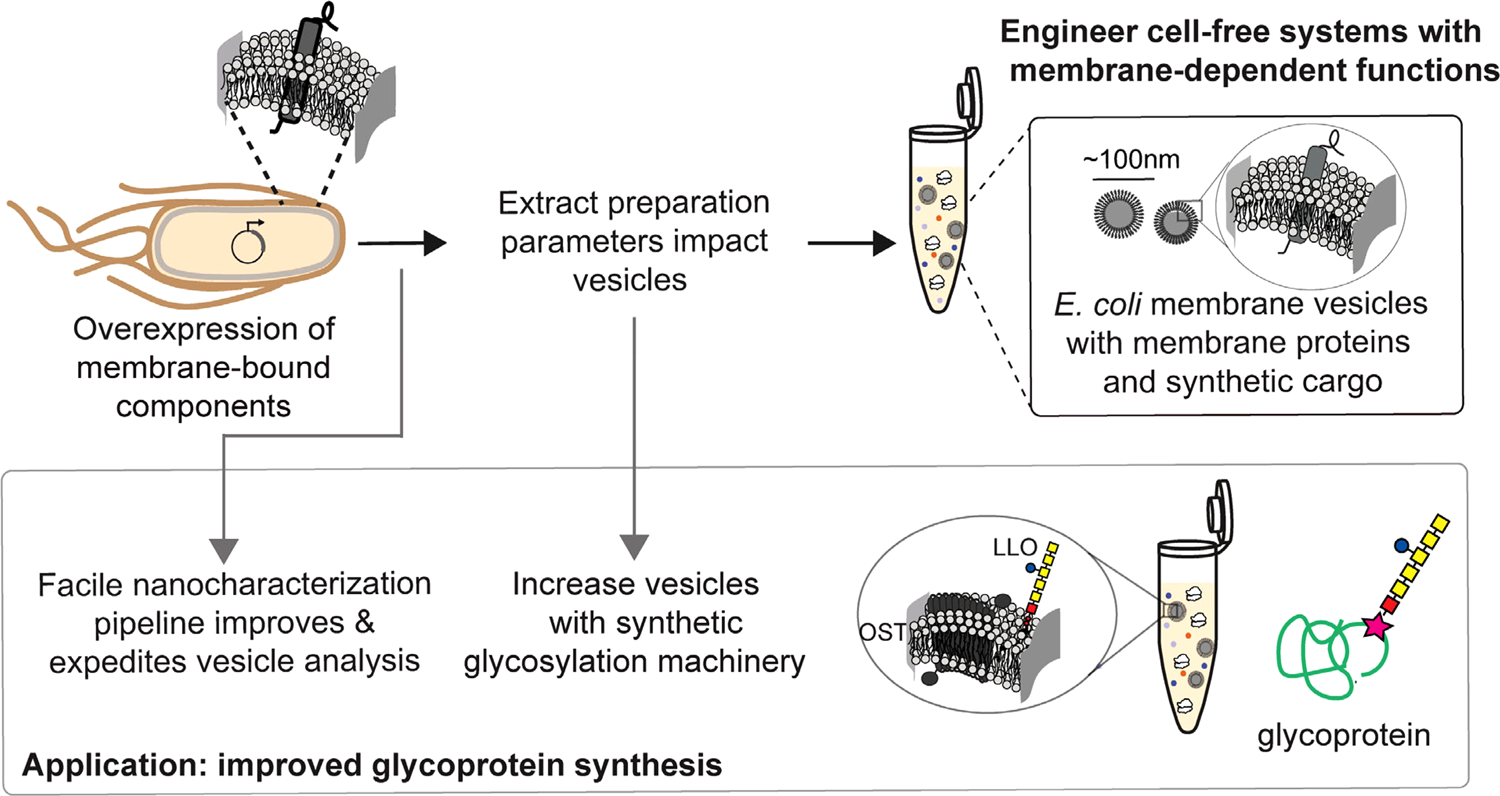
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles

Cell-Free DNA and Apoptosis: How Dead Cells Inform About the Living - ScienceDirect
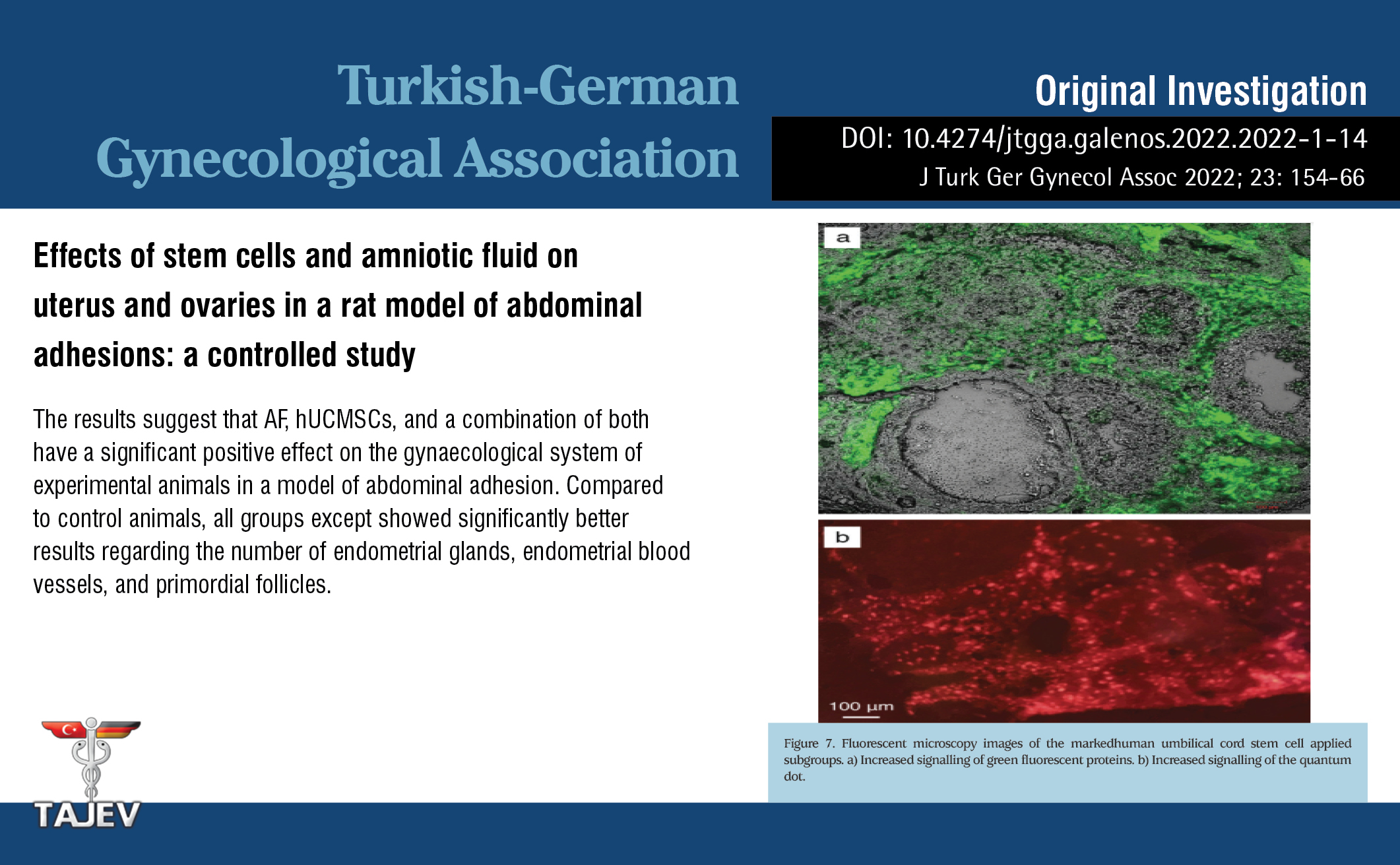
JTurkGerGynecolAssoc on X: Effects of stem cells and amniotic fluid on uterus and ovaries in a rat model of abdominal adhesions: a controlled study You can see the free full text of
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)