JSAN, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Remote health monitoring systems play an important role in the healthcare sector. Edge computing is a key enabler for realizing these systems, where it is required to collect big data while providing real-time guarantees. In this study, we focus on remote cuff-less blood pressure (BP) monitoring through electrocardiogram (ECG) as a case study to evaluate the benefits of edge computing and compression. First, we investigate the state-of-the-art algorithms for BP estimation and ECG compression. Second, we develop a system to measure the ECG, estimate the BP, and store the results in the cloud with three different configurations: (i) estimation in the edge, (ii) estimation in the cloud, and (iii) estimation in the cloud with compressed transmission. Third, we evaluate the three approaches in terms of application latency, transmitted data volume, and power usage. In experiments with batches of 64 ECG samples, the edge computing approach has reduced average application latency by 15%, average power usage by 19%, and total transmitted volume by 85%, confirming that edge computing improves system performance significantly. Compressed transmission proved to be an alternative when network bandwidth is limited and edge computing is impractical.

Superior Court of CA – County of San Joaquin – Superior Court of CA
JSAN, Free Full-Text
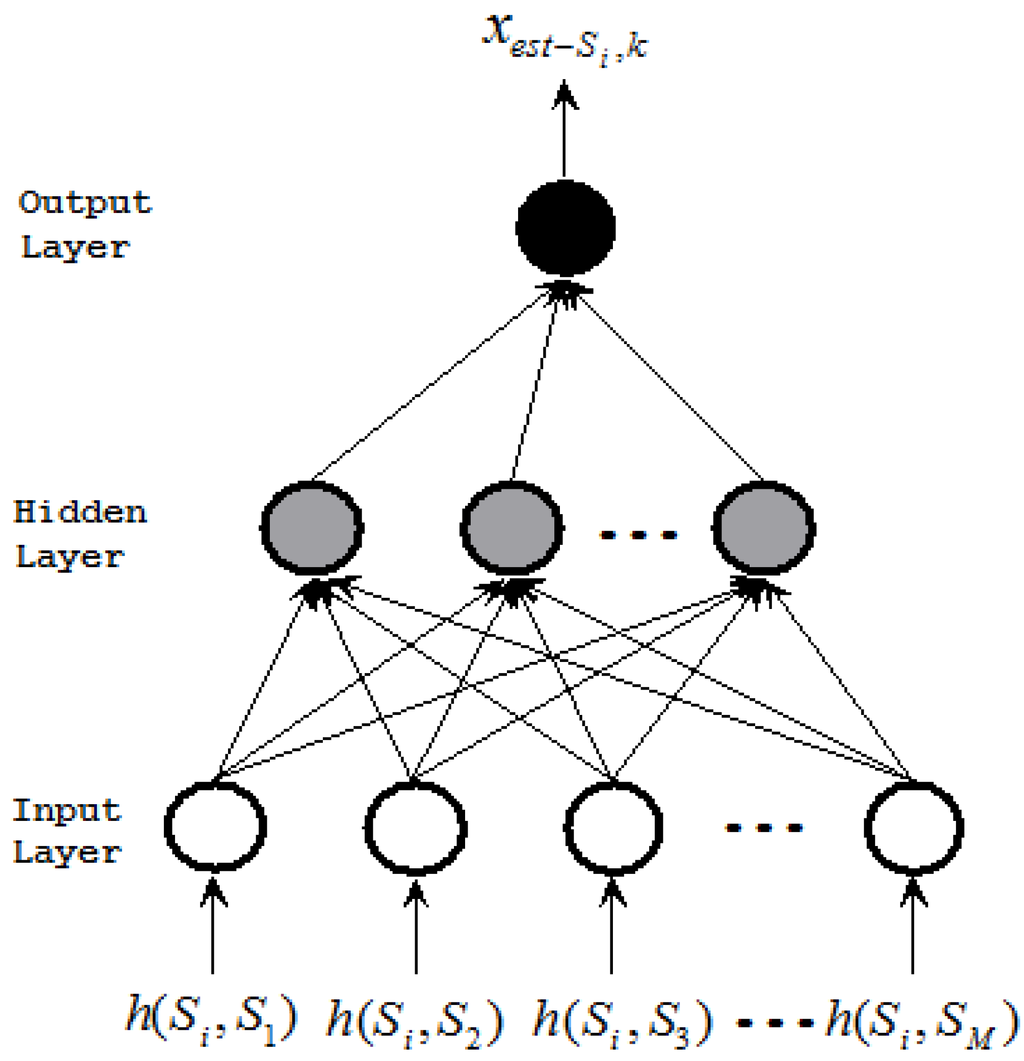
JSAN, Free Full-Text

JSON Schema
JSON Editor Online: edit JSON, format JSON, query JSON
TAPoR

Simple Travel Expenses Tracker Printable Work / Vacation
San José State University

MDPI Article Template - Overleaf, Online LaTeX Editor

Learn JSON - Full Crash Course for Beginners

Effects of sulfates on the hydration of Portland cement – A review

San Joaquin Valley APCD Home Page
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







