Open-Closed Principle – SOLID Architecture Concept Explained
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The Open-Closed principle (OCP) is one the 5 SOLID design principles. It was popularized by the American computer scientist and instructor, Robert C. Martin (aka Uncle Bob) in a paper he published in 2000. The other 4 SOLID design principles are: * Single Responsibility Principle (SRP) * Liskov
The Open-Closed principle (OCP) is one the 5 SOLID design principles. It was popularized by the American computer scientist and instructor, Robert C. Martin (aka Uncle Bob) in a paper he published in 2000. The other 4 SOLID design principles are: * Single Responsibility Principle (SRP) * Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP) * Interface Segregation Principle (ISP) * Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP). If you want to learn about all these principles, you can read my tutorial on the SOLID
The Open-Closed principle (OCP) is one the 5 SOLID design principles. It was popularized by the American computer scientist and instructor, Robert C. Martin (aka Uncle Bob) in a paper he published in 2000. The other 4 SOLID design principles are: * Single Responsibility Principle (SRP) * Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP) * Interface Segregation Principle (ISP) * Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP). If you want to learn about all these principles, you can read my tutorial on the SOLID

Open Closed Principle in Java with Example
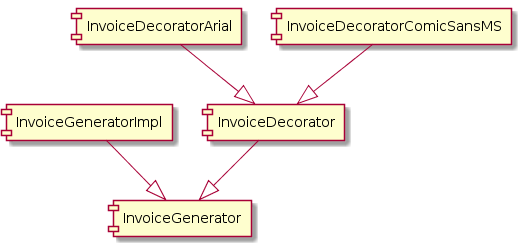
The SOLID Principles: a Guide for Object-Oriented Design - Data

Solid Principles – Java Questions
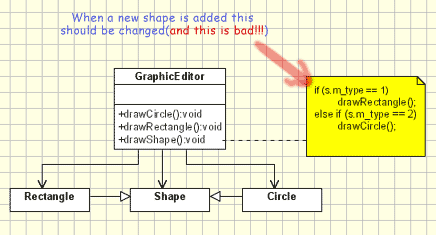
Open Closed Principle Object Oriented Design
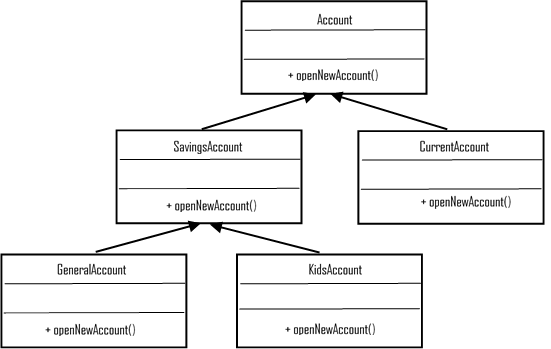
Open and close principle – SOLID - Architectural Patterns [Book]

SOLID Principles-The Open Closed Principle - JavaTechOnline

Open Closed Principle Explained - SOLID Design Principles

Single Responsibility in SOLID Design Principle - GeeksforGeeks

The Open-Closed Principle Explained

Learn Liskov Substitution Principle in C# (+ Examples) - DEV Community
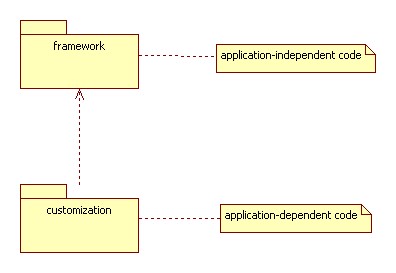
The Open-Closed Principle
Why open-closed principle is important - Scientific Programmer
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)