α-Synuclein Aggregation in Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, is characterized by the accumulation of protein deposits in the dopaminergic neurons. These deposits are primarily composed of aggregated forms of α-Synuclein (α-Syn). PD is a complex pathology initially associated with motor deficiencies, as a result of an acute neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), with a significant dopaminergic (DA) impairment.

Active alpha-synuclein proteins
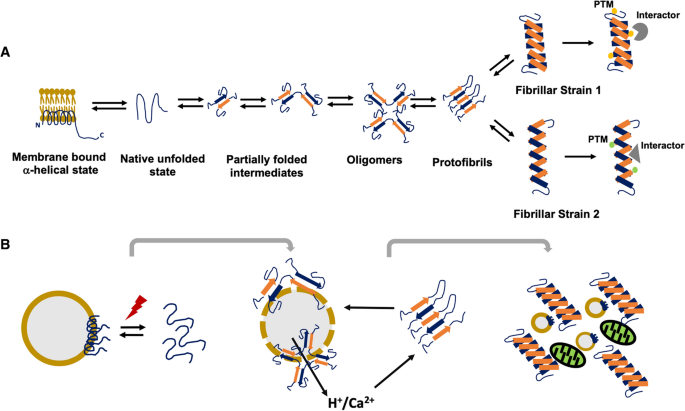
Initiation and progression of α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease
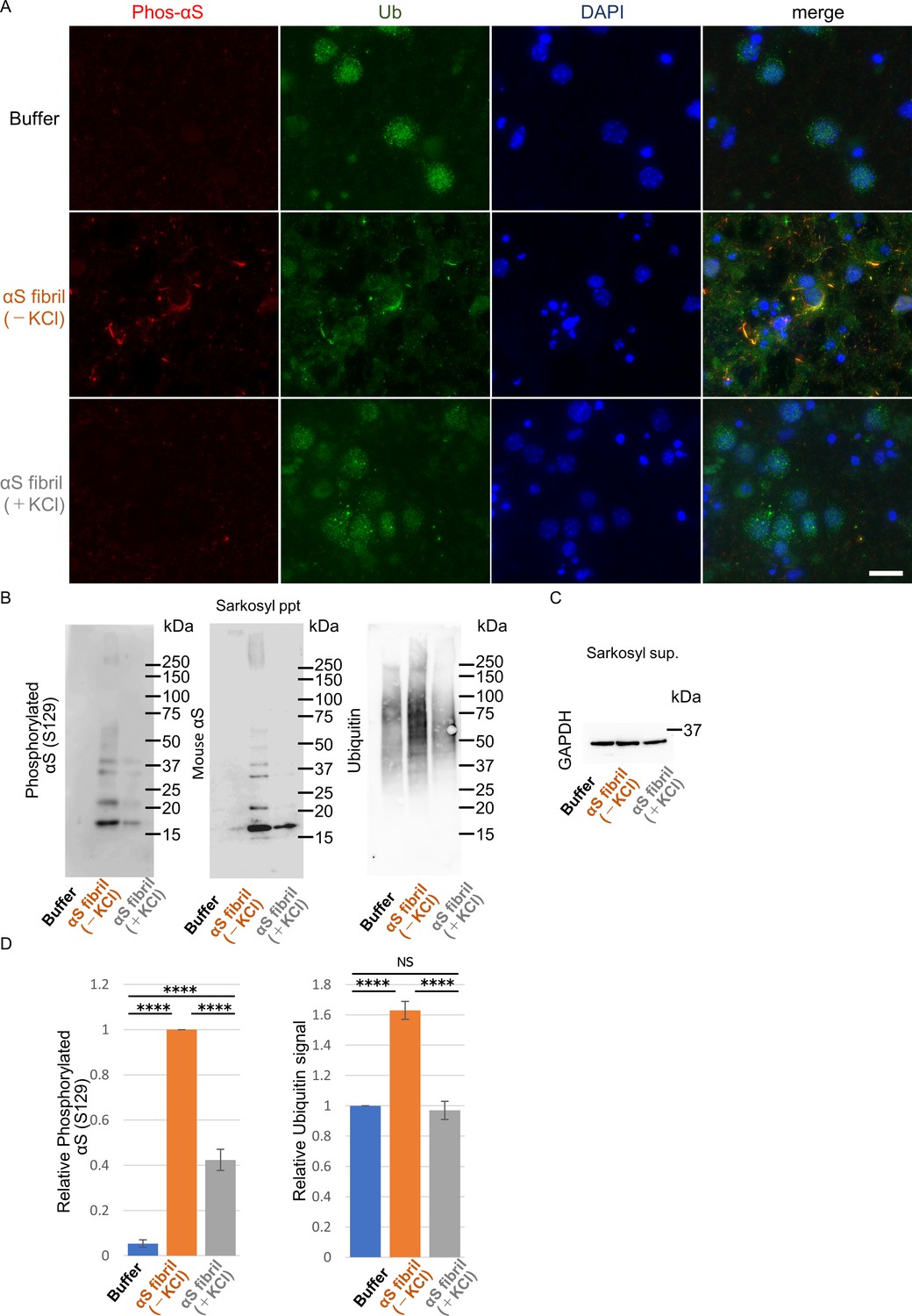
α-synuclein strains that cause distinct pathologies differentially inhibit proteasome
Novel and rapid device opens new doors for Pa

Aggregated α-Synuclein Mediates Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity In Vivo

Therapeutic functions of astrocytes to treat α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease

Pathological pathway of α-synuclein aggregation. Abnormal misfolded
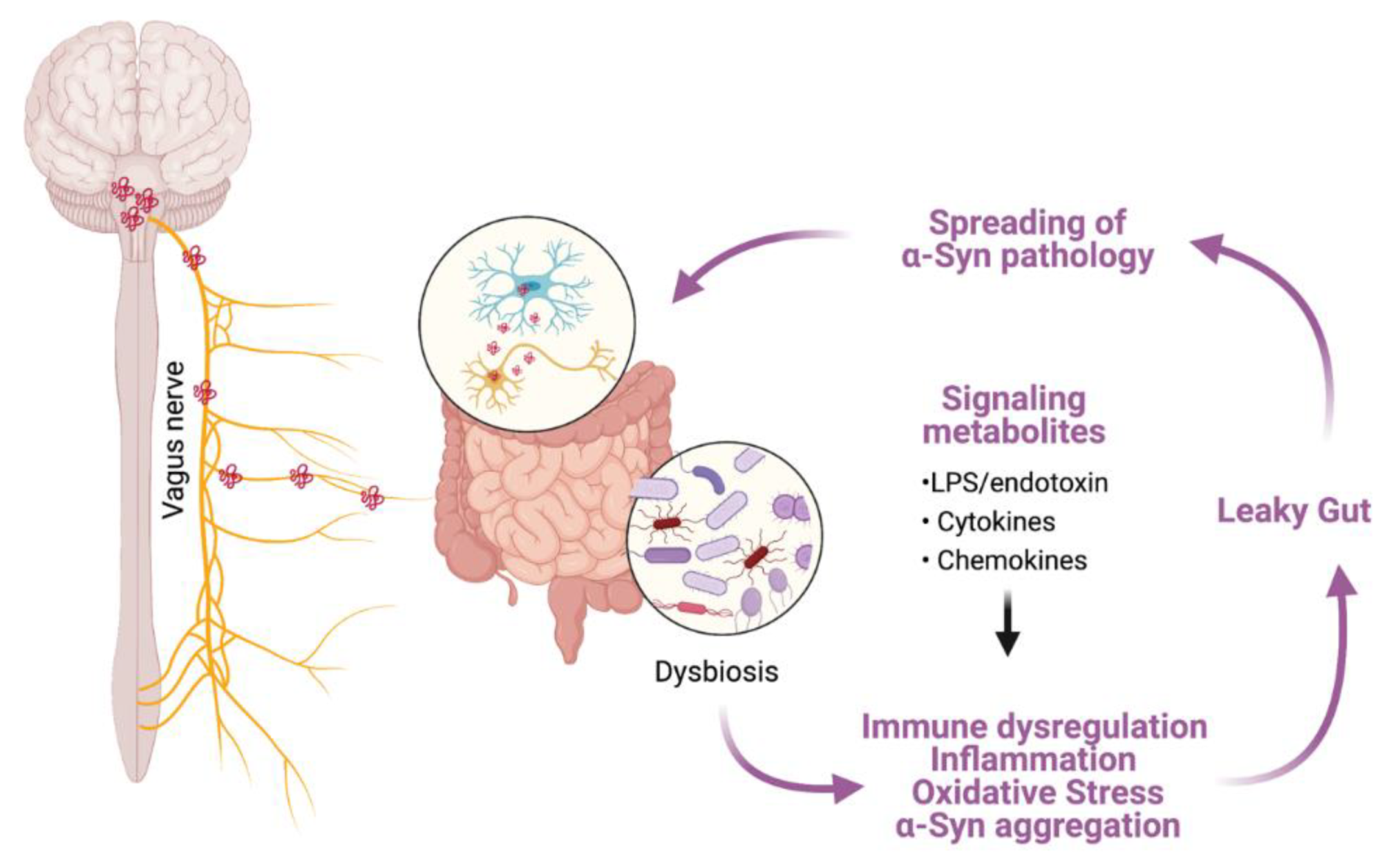
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Identification of a highly neurotoxic α-synuclein species inducing mitochondrial damage and mitophagy in Parkinson's disease
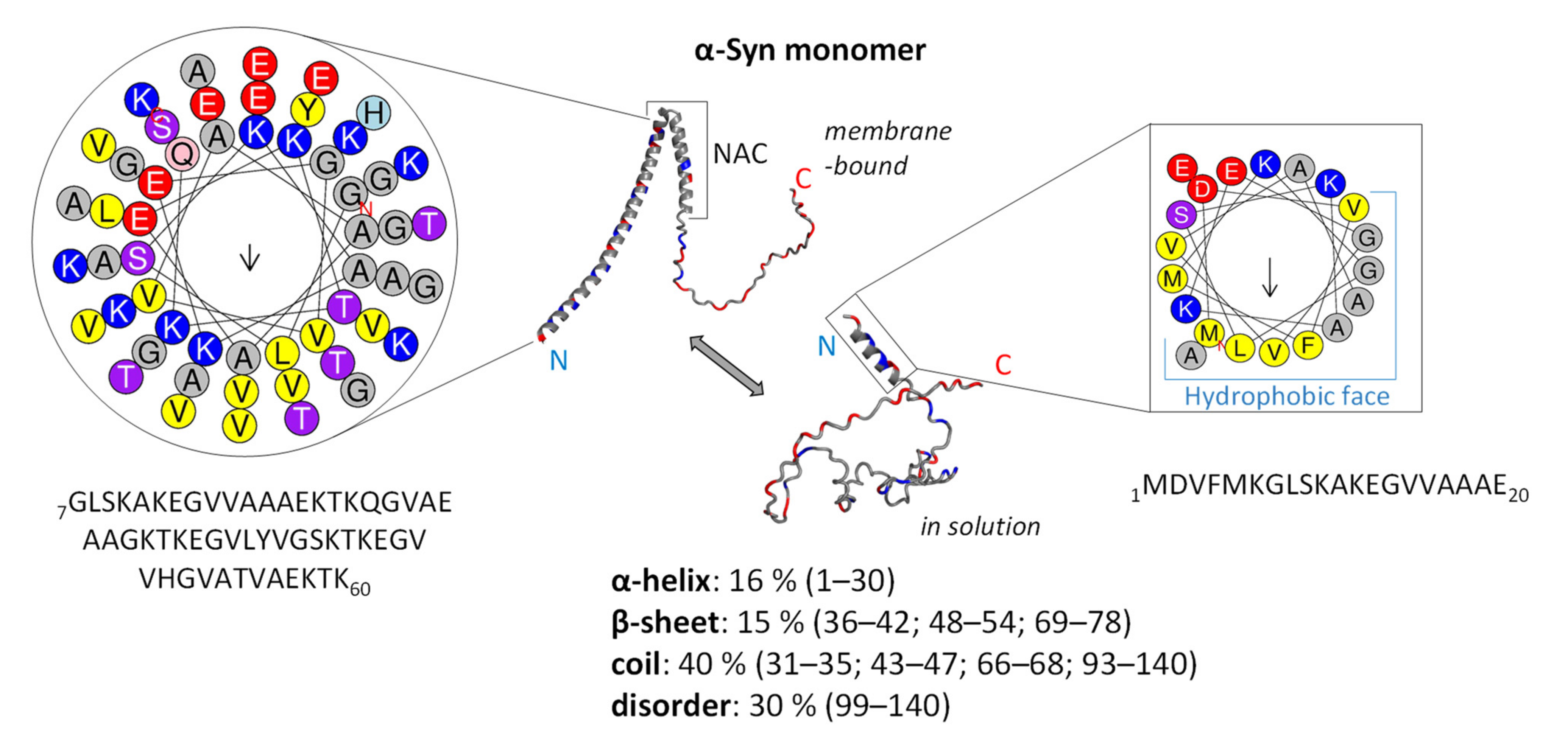
Cells, Free Full-Text

α-Synuclein Aggregates Increase the Conductance of Substantia Nigra Dopamine Neurons, an Effect Partly Reversed by the KATP Channel Inhibitor Glibenclamide

Targeting Alpha-Synuclein in the Gut May Slow Down Parkinson's Disease
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)