Next Generation Bipolar Plates for Automotive PEM Fuel Cells
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The results of a successful U.S. Department of Energy (DoE) funded two-year $2.9 MM program lead by GrafTech International Inc. (GrafTech) are reported and summarized. The program goal was to develop the next generation of high temperature proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell bipolar plates for use in transportation fuel cell applications operating at temperatures up to 120 °C. The bipolar plate composite developed during the program is based on GrafTech’s GRAFCELL resin impregnated flexible graphite technology and makes use of a high temperature Huntsman Advanced Materials resin system which extends the upper use temperature of the composite to the DoE target. High temperature performance of the new composite is achieved with the added benefit of improvements in strength, modulus, and dimensional stability over the incumbent resin systems. Other physical properties, including thermal and electrical conductivity of the new composite are identical to or not adversely affected by the new resin system. Using the new bipolar plate composite system, machined plates were fabricated and tested in high temperature single-cell fuel cells operating at 120 °C for over 1100 hours by Case Western Reserve University. Final verification of performance was done on embossed full-size plates which were fabricated and glued into bipolar plates by GrafTech. Stack testing was done on a 10-cell full-sized stack under a simulated drive cycle protocol by Ballard Power Systems. Freeze-thaw performance was conducted by Ballard on a separate 5-cell stack and shown to be within specification. A third stack was assembled and shipped to Argonne National Laboratory for independent performance verification. Manufacturing cost estimate for the production of the new bipolar plate composite at current and high volume production scenarios was performed by Directed Technologies Inc. (DTI). The production cost estimates were consistent with previous DoE cost estimates performed by DTI for the DoE on metal plates. The final result of DTI’s analysis for the high volume manufacturing scenario ($6.85 /kW) came in slightly above the DoE target of $3 to $5/kW. This estimate was derived using a “Best Case Scenario” for many of the production process steps and raw material costs with projections to high volumes. Some of the process improvements assumed in this “Best Case Scenario” including high speed high impact forming and solvent-less resins, have not yet been implemented, but have a high probability of potential success.

Basic structure of typical integrating PEMFC stack with end plate

Bipolar Metal Plate for Fuel Cell - PEMFC,PEM,Alternative energy

Proton-exchange membrane fuel cell - Wikipedia
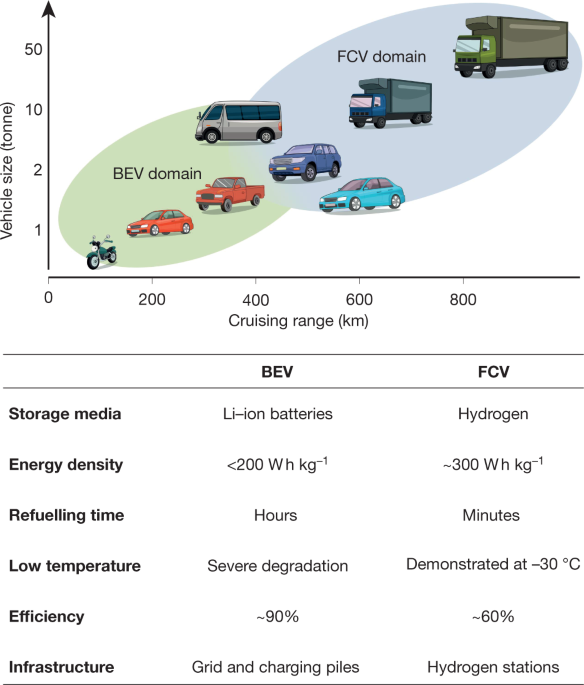
Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel

Start-up Precors develops innovative coating technology for high

Bipolar Plate Manufacturer for Fuel Cells & Electrolysers
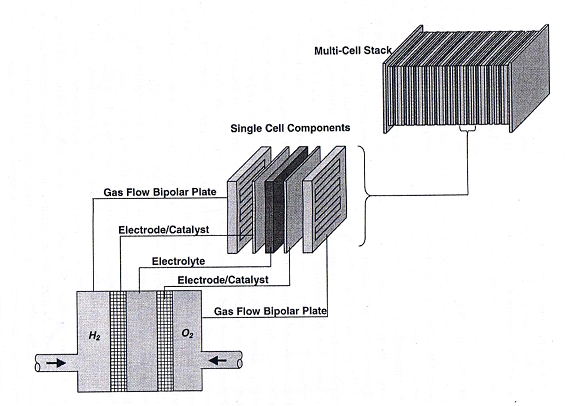
Electrochemistry Encyclopedia � PEM fuel cells
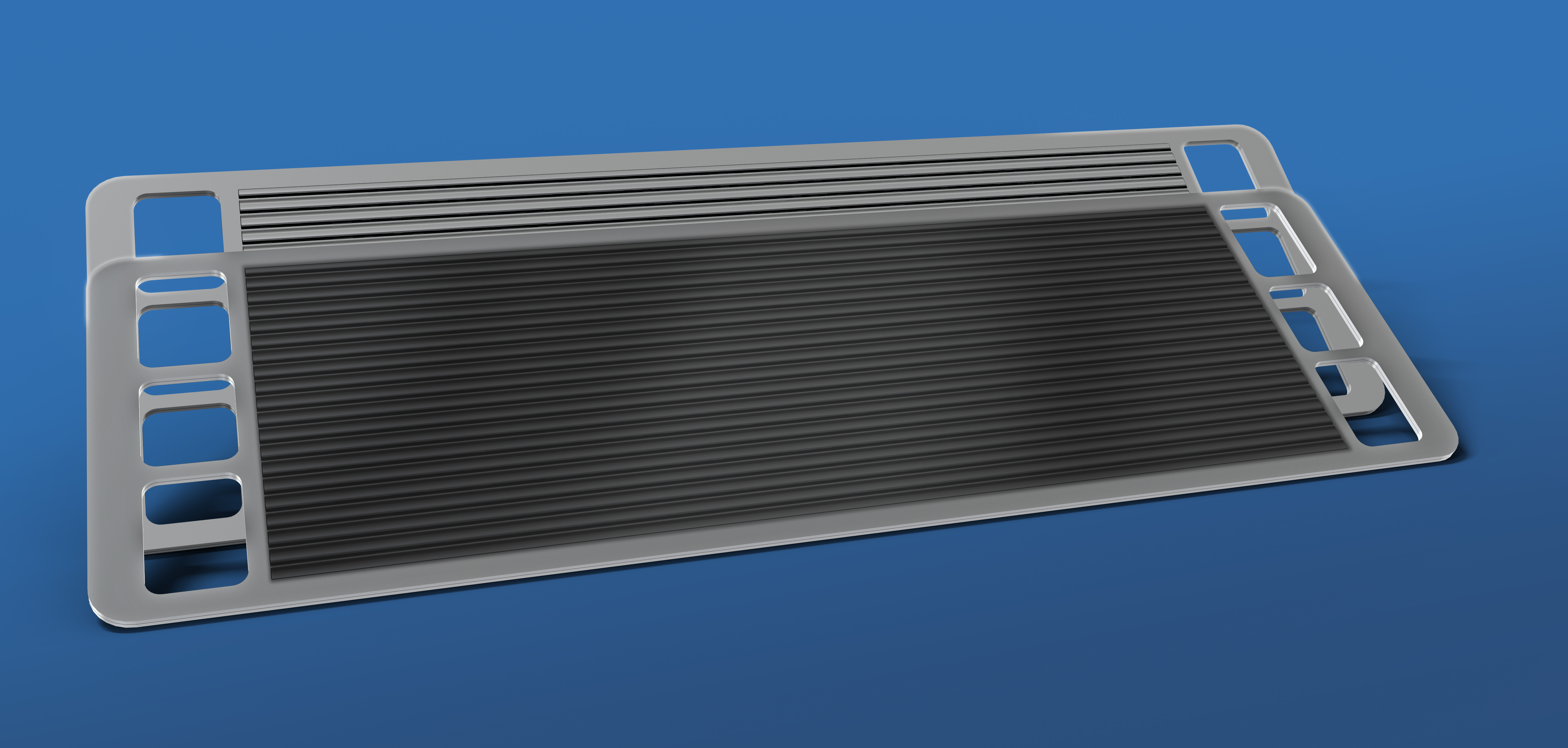
Graphite instead of gold: Thin layers for better hydrogen cars
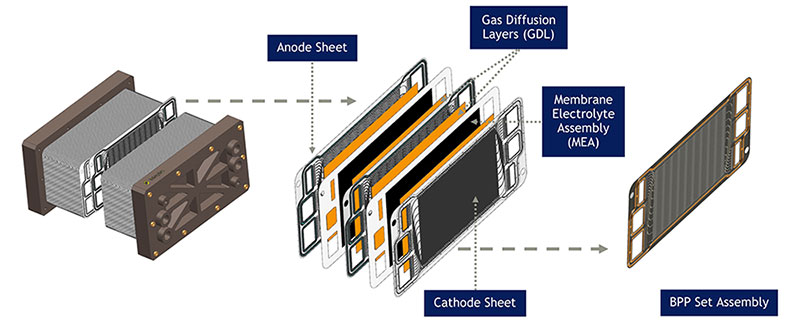
资源 Bipolar Plates and Their Critical Role in Fuel Cells
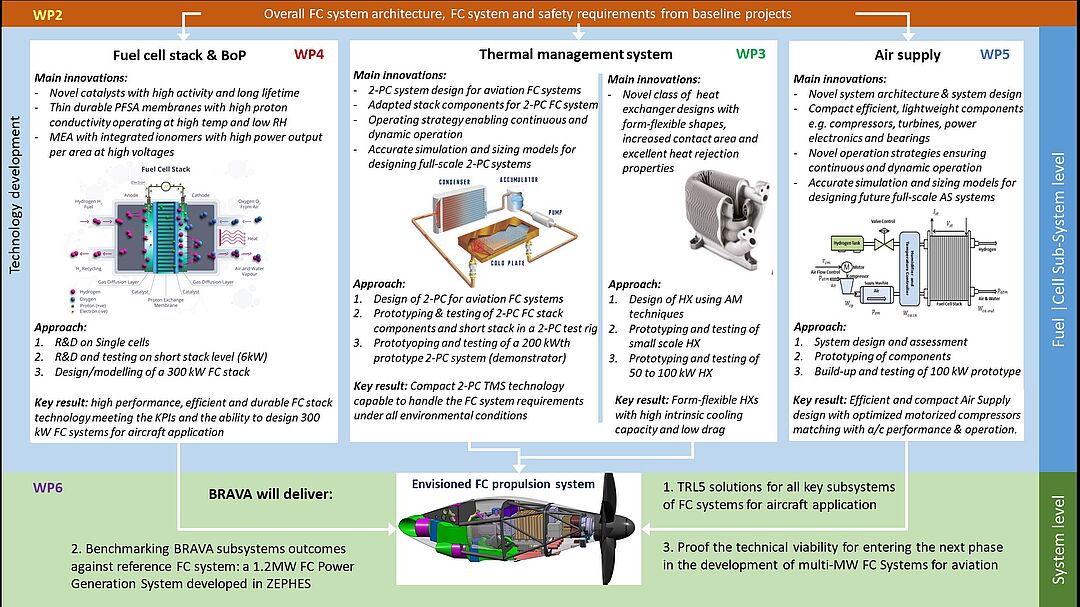
Research Projects

A comprehensive comparison of state-of-the-art manufacturing

IAA Mobility 2021: EKPO presents several new generation fuel cell
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






