Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
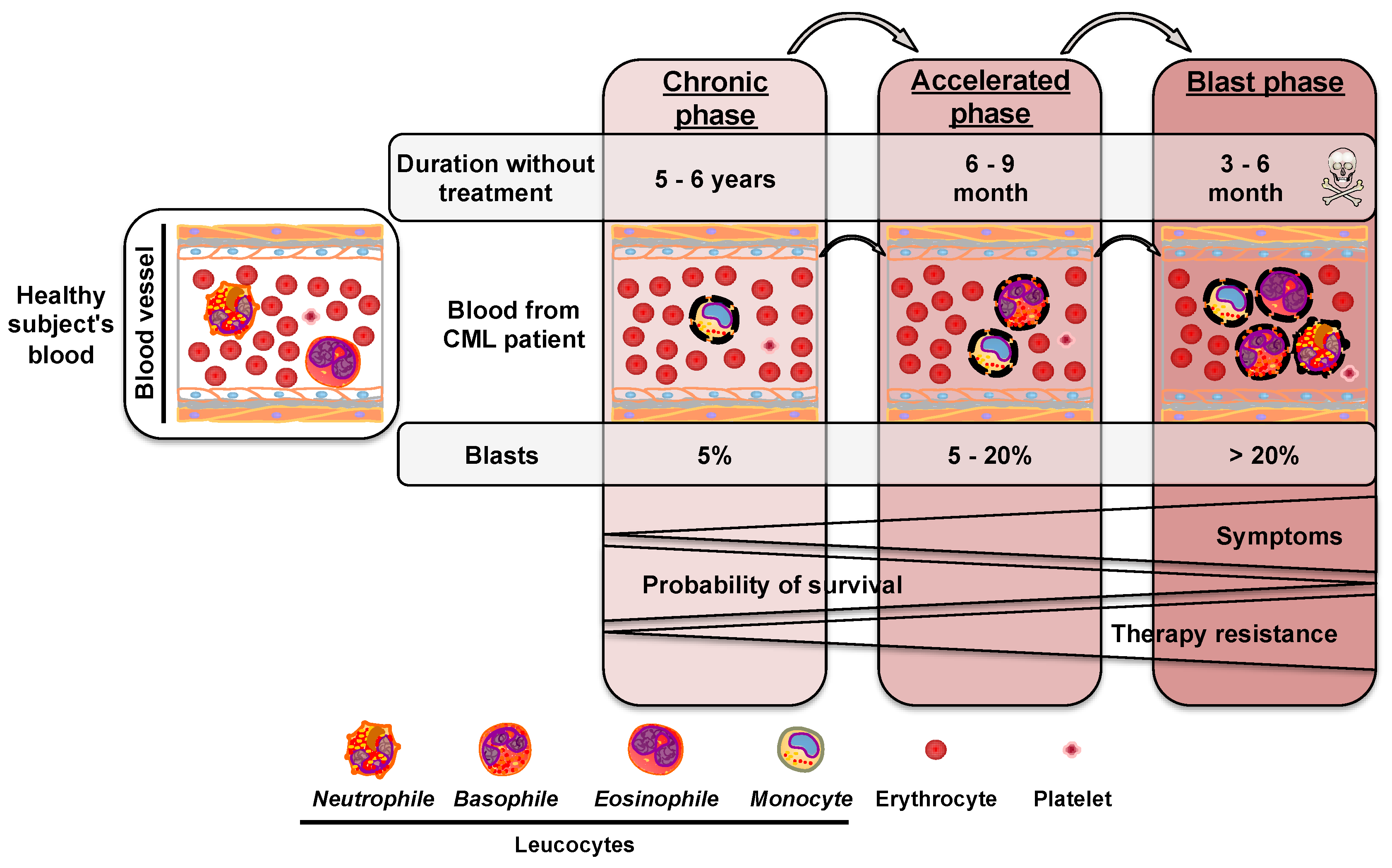
Background Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease with persistent synovitis. In the present study, the impact of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) was explored to determine methods for the diagnosis and treatment of RA. Methods First, fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) were obtained from a collagen-induced rat RA model. Next, MCP-1-overexpression plasmid and small interfering RNA were transfected into human and rat FLSs. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), Transwell migration and flow cytometry assays were used to analyze cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis of FLSs following MCP-1 transfections, respectively. Furthermore, western blotting was used to analyze the expression levels of p-P38, p-PI3K, PI3K, CD31, VEGF, TNF-α and IL-β in FLSs following MCP-1 transfection. In addition, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and ELISAs were used to analyze the expression levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), estrogen receptor, MCP-1 and pentraxin-3 in patients with clinical RA, followed by correlation analysis of clinical data. Finally, expression validation, diagnostic and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis of MCP-1 were performed. Results MCP-1 promoted FLS proliferation and migration, and affected the apoptosis of FLSs. In addition, the expression levels of p-P38, p-PI3K, PI3K, CD31, VEGF, TNF-α and IL-β were also affected by MCP-1. In patients with clinical RA, the expression level of MCP-1 was increased. Moreover, CRP expression level was significantly up-regulated in RA. Clinically, MCP-1 was strongly correlated with tender joint count, swollen joint count, visual analog scale for general health and disease activity score 28 (DAS28)-MCP-1, and was moderately correlated with DAS28 and DAS28-CRP. PPI analysis showed that MCP-1 mainly interacted with other inflammatory cytokines. Conclusion In conclusion, MCP-1 may play a significant regulatory role in RA, and could be used as a measurement index of clinical RA activity.
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://www.mdpi.com/diagnostics/diagnostics-09-00098/article_deploy/html/images/diagnostics-09-00098-g007.png)
Diagnostics, Free Full-Text
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://www.ijbs.com/v19/p0281/toc.jpg)
Nesfatin-1 Stimulates CCL2-dependent Monocyte Migration And M1 Macrophage Polarization: Implications For Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC7226834/bin/cells-09-00880-g003.jpg)
Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. - Abstract - Europe PMC
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1007%2Fs11033-023-08277-9/MediaObjects/11033_2023_8277_Fig2_HTML.png)
Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells therapy for rheumatoid arthritis - a concise review of past ten years
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0753332222002359-gr1.jpg)
The enhanced mitochondrial dysfunction by cantleyoside confines inflammatory response and promotes apoptosis of human HFLS-RA cell line via AMPK/Sirt 1/NF-κB pathway activation - ScienceDirect
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://media.springernature.com/full/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41392-023-01467-8/MediaObjects/41392_2023_1467_Fig1_HTML.png)
Targeting strategies for bone diseases: signaling pathways and clinical studies
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/cms/asset/bfd3f276-4d0c-41f3-b3aa-8a3c2c146bff/cei13228-fig-0002-m.jpg)
Altered metabolic pathways regulate synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis - Fearon - 2019 - Clinical & Experimental Immunology - Wiley Online Library
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://www.medrxiv.org/content/medrxiv/early/2020/07/19/2020.07.16.20155291/F7.large.jpg)
Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid neutrophils drive inflammation through production of chemokines, reactive oxygen species and neutrophil extracellular traps
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41598-021-01692-7/MediaObjects/41598_2021_1692_Fig4_HTML.png)
Phenotypic and functional characterization of synovial fluid-derived fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://www.tandfonline.com/cms/asset/6d33527f-fb48-4fd4-8386-45f69ddff2ad/kgmi_a_2263207_f0001_oc.jpg)
Full article: Progress of linking gut microbiota and musculoskeletal health: casualty, mechanisms, and translational values
![Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]](https://dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net/2021/11973/1/fig-10-full.png)
Exploring the role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [PeerJ]
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)